The concept of a business model
Business model is a short and succinct idea of how a company turns its product or service into profit. Business model gives answers to the questions: what is the global purpose for which the company was created and exists on the market, how its internal structure is arranged and all business processes - from product creation to its implementation - are interconnected.
Business model operates with such a notion as value, and demonstrates how the company creates value for customers and itself. Value for customers is a benefit they receive by using a product or service, their feelings, emotions and benefits. Value for the company is the profit it makes.
At the center of every business model is always the customer and the value. The business model explains what value the business provides to the customer, how this value should be presented to the company and implemented, maximizing profit.
Components of the business model:
- Product: what exactly the company offers as value to the customer, how it creates that value, and how it sells it
- Target audience: who exactly purchases the product, what kind of people they are, what their interests and needs are
- Flow of funds: how the customer buys the product, and the company makes a profit.
Business models can be generic, simple or complex. With the development of personal digital technology and the global Internet, more complex successful business models based on multiple online sales channels began to emerge.
How to develop an effective business model for the company
Before you choose the business model that will bring you the most profit, you should conduct a thorough competitive intelligence, market analysis and analysis of the current company structure. Matching a company's goals to its industry position, resources, external and internal capabilities is the main basis for developing a successful business model for any business.
To determine which business model will be most effective for you, you should go through several stages of research, carefully systematize the results and answer important questions:
- Analyze the industry as a whole and the business models presented in it
It is necessary to determine how the business processes in your industry are arranged, conduct competitive intelligence, make a hierarchy of competitors and find out who is the leader, a contender for the leadership or a follower. Analyze your competitors' business models by identifying their strengths and weaknesses, and draw a parallel between your business model and your market share. Systematization of information on how and why industry leaders change positions can provide important insights. - Analyze the company's existing business model
Armed with the data obtained during the previous stage of the research, it is necessary to assess how successful the business model of the company is, which defines its current activity. An analysis should be made of the business processes and competitive advantages, highlighting their difference or similarity to the unique selling proposition of major market players. It is important to understand which advantages need to be strengthened and which market competencies need to be developed.
- Define the company's global purpose and mission
A company's mission is its philosophy. The main reference point that defines why the company exists, what drives and motivates it to create value for customers. At this stage it is necessary to define what global goals drive the company and how the existing business model helps to achieve them, what helps the company to stand out among the competitors, to produce a truly unique and in-demand product. - Define the new business model
Using the most successful example of a business model in your chosen niche as a reference point, identify the main components of the new business model applicable to your business. To determine the position of this model in the industry, to predict the economic efficiency. To carry out SWOT-analysis. Justify the main parameters of the business model. - Specify and implement the new business model
To compare the strengths and weaknesses of the old and new business model, to determine the optimal arrangement of production, mechanisms for innovation, promotion and sales channels of the product. To outline the business management system.
Such an accurate and complete analysis allows you to take a fresh look at the mechanics of the company's activities and evaluate the effectiveness of its work. Competent systematization of the obtained data will help to develop an effective and most profitable business model for your company, consider growth points and new promising vectors of further development.
Types of business models
The most complete and up-to-date classification presents 10 basic types of business models, significantly different from each other in their approach to the organization of business processes and the mechanics of making a profit.
- Manufacturer. The main task of a business of this model is to produce tangible goods that are in demand by consumers and distribute them through the most efficient distribution channels. A manufacturer creates goods (for example, accessories, gift boxes, bouquets), intellectual property products (artistic photography, mobile application, musical composition) and services (legal, accounting support, auditing, consulting services, etc.).
- Distributor. The task of distributors (intermediaries) is to distribute the manufacturer's goods in wide retail or wholesale lots. In this business model, the intermediary, as a rule, combines the goods of several manufacturers to meet the widest demand. Intermediaries make a profit by increasing margins and optimizing logistics costs.
- Franchising. This business model involves the implementation of an already ready and successful business model under the terms of an official license. A successful business (for example, a restaurant, cellular operator, postal delivery service) sells permission to open a point of sale under the name of its brand. Under this model, the business (franchise) owner receives profit in the form of timely payments from the franchisee (franchise buyer). Such payments are called royalties. Franchising is a profitable business model, as the franchisee's start-up risks are minimal, while brand recognition and popularity guarantee high sales.

- Brokerage. This business model brings together buyers and sellers in different sectors, whether B2B or B2C, and conducts transactions between them. The broker's profit is a percentage of the transaction or a fixed rate. The main features of the brokerage business model are scale and network effect. However, it will be successful and bring the owners a huge profit if there are enough active buyers and sellers. An example of a successful brokerage business model is Amazon.
- Leasing. The essence of this business model is that the company-owner rents out goods, machinery, equipment or premises to other companies or individual entrepreneurs for entrepreneurial activity. The landlord's profit is to receive a fixed fee for the use of the retail space, goods or tools. The most popular and understandable example of a landlord business model is a shopping mall.
- Advertising. The advertising business model involves the creation of an online or offline platform that attracts advertisers. For example, a news site or a printed glossy magazine. The popularity of the resource created is calculated in terms of traffic or the number of copies sold. The more popular the resource (the higher quality content created and placed on it), the more advertisers will want to place their ads, providing profit to the resource owner.
- Affiliate. A business model that gained a new round of popularity with the development of Internet technologies. The mechanics of making a profit is to sell the company's main service (e.g., hosting) and attract a client to an affiliate program, offering him a commission for each transaction made through his mediation. For example, by ordering hosting, you distribute a referral link to the resource hosting company and get a profit - a percentage of hosting sales made by clicking on "your" link. An example of the affiliate model can be the distribution of promotional codes for services and products by popular bloggers to their subscribers.
- Subscription-based (prepaid) business model. Having created a product or service, the producer receives profit at the expense of periodic payments from users. In the twentieth century, this business model was successfully used by periodicals, in the twenty-first century - by specialized information, analytical Internet resources, software developers and service providers.
- Multi-level. The business model of network marketing, which involves the transformation of consumers into sellers and the creation of several levels of sellers, based on their activity in sales. For example, the buyers of Avon and Amway become sellers of the brand's products, selling them among acquaintances and friends. The most active salespeople rise to the highest level in the distributor hierarchy.
- Razor and Blade model. The business model involves making a profit from the difference in the selling price of the main product (for example, an electric razor) and a companion product (a replacement cassette for an electric razor, the price of which can be 50% of the price of the main product). For such a business model to be profitable, it is necessary to protect one's own developments with an intellectual patent in order to avoid competitors producing the accompanying product.
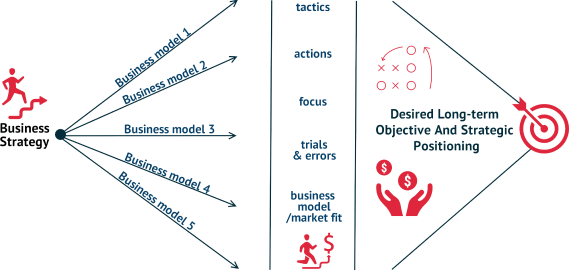
How business models differ from business strategies
The most common mistake is the substitution and equation of the concepts of business model and business strategy. In fact, these definitions are closely related, but not equal to each other.
The main differences are determined by three main factors:
- How value is created (for the client and the company) and turned into revenue
Business model provides a clear plan of action and an answer to the question: how does the company create value (goods or services), where and to whom does it sell, making a profit. Business strategy gives an idea of how to act in order to be unique among competitors and create a sought-after product and profit from its sale. - The cost of commercial activity and the owner's profit
The business model of the project will clearly show, out of what the price of the goods is formed. The business strategy will highlight the methods and volumes of financing: how much and from where to attract investments for the fastest payback of a project and profit making. - The level of team preparation
To develop a business model for a company, it is sufficient to methodically conduct market research and analyze the results. To develop a business strategy, the team must have in-depth knowledge of the market and practical experience in a particular industry of entrepreneurship.